
[image description: a photo of a middle-aged transmasculine person in a van, half-rendered into a sketch, using the Heisenberg setting in Prisma, turned down to 54%. Copyright 2016, Sparrow R. Jones]
I don’t like to engage in serious conversations on Twitter because I’m so quickly overwhelmed by the format, but yesterday I ended up in a corner of a discussion that spread throughout much of the Twitter Autistic community, as evidenced by this other excellent blog post addressing a different aspect of the conversation: Autism does not reside in a medical report.
My corner of the conversation centered around the question of whether autism is a disability or not. The same person who stirred Sonia Boue to write the excellent post linked above got into it with one of my Twitter contacts on a different but related topic:
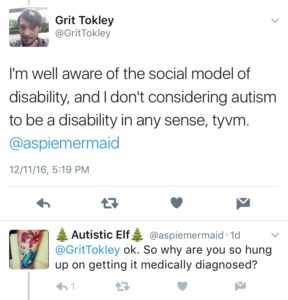
[image description: A twitter exchange. Grit Tokley writes: “I’m well aware of the social model of disability, and I don’t considering autism to be a disability in any sense, tyvm. @aspiemermaid” Autistic Elf (Aspiemermaid) responds: “@GritTokley ok. So why are you so hung up on getting it medically diagnosed?”]
Because, of course, the bulk of the following Twitter discussion centered around strong assertions that autism is not a disability, along with strong assertions that everyone is entitled to their own opinion and we must all agree to disagree
*sigh*
So, with that.
Three Models of Disability
There are many different models of disability, but I would like to focus in on three of them as being the most mainstream and/or the most useful for various groups of people.
The Medical Model of Disability
This is the most mainstream model of disability and the one you’re most likely to have seen before. One participant in the Twitter discussion shared this definition of disability that pretty well sums up the nicest version of the medical model you are ever likely to see:

[image description: a white background with black text reading: “Disability is an impairment that may be physical, cognitive, intellectual, mental, sensory, developmental, or some combination of these that results in restrictions on an individual’s ability to participate in what is considered “normal” in their everyday society.”
That’s the medical model and that’s why so many disabled people reject that definition of disability. But it’s still a really popular definition. And, as the person who shared the image pointed out, by this definition, autism is quite clearly a disability. Something like 99.9% of the Autistics you will meet have at least one of some kind of sensory issue that makes life difficult if/when they encounter sensory assaults (or situations in which they require extra sensory stimulation in order to stay regulated.) By definition, we are developmentally disabled, whether you use the medical model’s terminology (developmental delay) or recognize our development as being on a different trajectory from the mainstream. It’s pretty clear that, within the medical model we are disabled.
The Social Model of Disability
This is the model I see most often in the Autistic activist community. The social model was developed in the 1970s by British disability theorists who did not appreciate the way the medical model dumps all responsibility for disability and accommodations thereof in the laps of disabled people. The social model was a great improvement over the medical model, particularly in the area of human rights.
The social model posits that disability does not actually exist. Those states of being that are labeled as “disability” are natural variations in the human condition and all human beings require support and accommodation from society in order to survive. For example: you probably eat food that someone else grew, someone else processed and/or packaged, someone else drove to your region in a truck using fuel gathered and processed by someone else, driving on roads built by others and paid for collectively through taxation. All of the steps and people required to get food to the supermarket, farmer’s market, soup kitchen, restaurant, institutional kitchen or whatever location it is where you go to feed yourself are supports and accommodations that society approves of and works hard to keep in place.
When the need is a mainstream one, the supports and accommodations are called “infrastructure.” When the need is a divergent one, the supports and accommodations are called accessibility measures. According to the social model, “disability” is a social construct and “disabled” is what society is doing to you if it decides that the supports and accommodations you require are too much trouble and you are not worth the expenditure of time, energy, money, and other resources that would be required to make society accessible to someone like you.
Within the social model of disability, Autistics are disabled (by a society that does not value Autistics sufficiently to support and accommodate us) but autism is not a disability because disability does not exist, being merely a social construct that makes it convenient for those who would like to disable us without feeling guilty about it.
The Social-Relational Model of Disability
Finally, we have my favorite model of disability, the social-relational model. The social-relational model is less well-known, having only been developed in the 21st century, by disability theorist Solveig Reindal1. The need for the social-relational model was clear before Reindal wrote about it, though, and I’ve also noticed some people who are unaware of Reindal’s work trying to re-shape the social model into something closer to Reindal’s vision, due to dissatisfaction with the social model. No need to re-shape the social model, though, when the social-relational model already exists.
The major dissatisfaction activists and theorists were finding with the social model was that disabled people could not express any dissatisfaction with the experience of being disabled without being viewed as “traitors to the theory.”2. Reindal’s new formulation of the social-relational model moves to a third position in which society is still held accountable for disabling people but theory does not ignore the body or the real struggles some people have with disability, independent of society’s support and accommodations or lack thereof.
While the social model claimed that disability does not exist, being purely a social construct evolving out of views of those constructed as disabled as being “lesser” in some way, Reindal acknowledged that those who are identified as disabled do, indeed, have some type of impairment. These impairments – what the medical model calls “disability” – Reindal labeled as “barriers to doing.” In contrast to impairment, Reindal writes about “being disabled” as it is defined by the social model as the “barrier to being,” suggesting that the social constructs that view those with impairments as lesser beings, not worthy of inclusion or accommodation, creates an existential crisis that extends deeply into the disabled person’s core being.
Within the social-relational model, I have impairments (although not all Autistics have social-relational impairments, according to what others have told me) and I am disabled by society’s lack of support and accommodation for my needs. I have a disability and I am disabled. I have barriers to doing, which I find frustrating, and I have barriers to being, which I find devastating.
Why Is All This Important?
If you have read this far, you may be asking yourself why any of this matters. As an old friend used to say, “how will this help me shop for groceries?”
This is important because these are not just words and theories. This is important because these different frameworks for viewing people’s lives are the structures that underlie how we are treated, what assistance we get or do not get, even whether people feel we have sufficient humanity and “quality of life” to deserve to continue living. It is very important to understand these seemingly academic topics, because these sorts of thoughts are beneath the doctors’ attempts to deny Mel Baggs a feeding tube to keep Mel alive. These thoughts are behind the choice of those administering the transplant registries to deny Paul Corby a spot on the heart transplant list.
These questions and ideas and words are not just exercises in navel-gazing. They are the basis upon which life-or-death decisions are made about us. Too often these decisions are made without us, because the operating definition of disability/disabled is one that places us in an infantilized position where we are not considered able even to advocate for ourselves.
When I turned to my Facebook friends and asked how they felt about the question of whether autism is a disability or not, I got an overwhelming flood of responses — there were over 200 responses to the question. That discussion really helped me in shaping my thoughts about the rather distressing day I had on Twitter and the nature of disability/being disabled.
Two comments in particular resonated very strongly with me. I found them both thought-provoking and comforting after all the Twitter distress.
Cas Faulds said: “our current society and our current systems means that we are disabled and if we’re working under the impression that we aren’t, we’re setting ourselves up for failure.”
That’s very important. Denying that we are disabled (which I see a lot of Autistics doing these days) runs the risk of setting ourselves up for failure when we decide that there is no real difference between Autistic and non-autistic. This opens the door for the struggle I’ve faced most of my life, believing I kept failing because I just wasn’t trying hard enough. Understanding that I am disabled has helped me to forgive myself for those very real things I just can’t do — whether due to inherent impairment or being disabled by society.
No matter how “disabled” is philosophically constructed, I am definitely disabled and acknowledging that fact gives me the space to re-frame situations and figure out accommodations, whether self-accommodations or accommodations I request from others.
My friend, Chris, said: “there’s an immense spectrum, from not disabling to severely disabling, and someone pretending their end is the only one that should be called “autism” — well that’s pinging ME really hard as supremacism.”
Yes! The people who kept telling me that autism is not a disability and Autistics are not disabled said that I would hurt the image of autism by insisting that it is a disability or that Autistics are disabled. I felt very excluded and erased because I am quite disabled.
When the discussion was framed in terms of division and supremacism, the first thing I thought of was Michael John Carley’s distress about dropping Asperger’s from the DSM because he didn’t want to be mistaken for someone with more challenges.
The people on Twitter might be right. It might just be a matter of opinion. It might be that autism is not a disability (“but you can call yourself disabled if you want to.”) It might be that we should just all “agree to disagree.”
But I think we should tread carefully on declaring that autism is not a disability when there are so many of us who are so very clearly disabled., regardless of which model of disability one chooses. I know that I would rather be mistaken for “somebody who might have to wear adult diapers and maybe a head-restraining device” (to quote Carley) than throw my Autistic siblings under a philosophical bus because my support needs are different from theirs.
So….my stance? Autism is a disability. Autistics are disabled. Society needs to work harder to support and accommodate us all, in all our variety, with all our different types and levels of support needs. We are human beings, expressing part of the infinite diversity humans express in infinite combinations. Accept us. Support us. Value us. The fact that we are disabled only means that society needs to think more carefully and work more diligently to craft an accessible world we all can live in, together.
1. Reindal, Solveig Magnus. 2008. “A Social Relational Model of Disability: A Theoretical Framework for Special Needs Education?” European Journal of Special Needs Education 23 (2): 135-46.
2. Shakespeare, Tom, and Nicholas Watson. 2002. “The Social Model of Disability: An Outdated Ideology?” Research in Social Science and Disability 2: 9-28.
and
Thomas, Pam, Lorraine Gradwell, and Natalie Markham. 1997. “Defining Impairment within the Social Model of Disability.” Coalition Magazine July.




Recent Comments